
 Another tool from the A* Vienna software team
Another tool from the A* Vienna software team
AnisoCADO is the python package created around Eric Gendron’s code for analytically generating field-varying SCAO PSFs for the ELT.
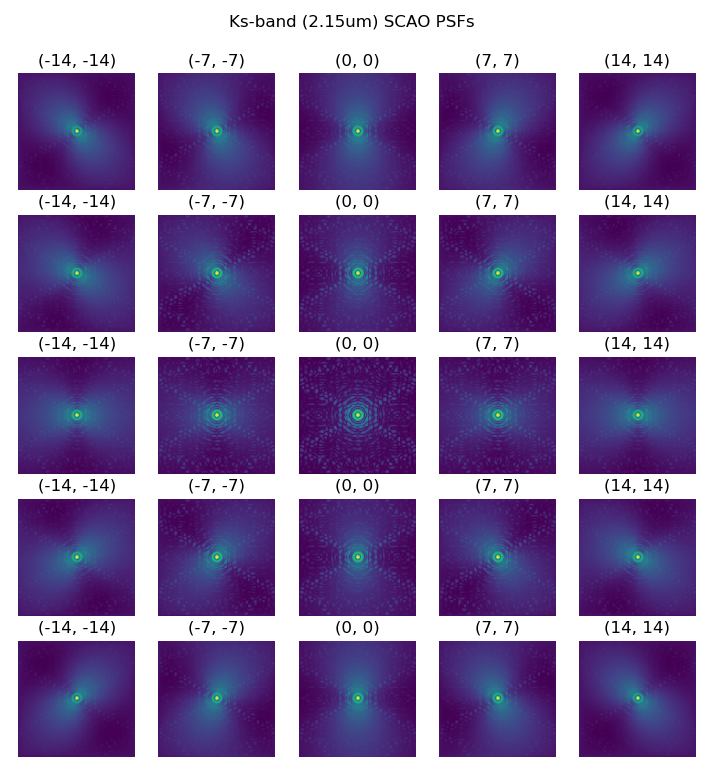
A grid of SCAO PSFs at 2.15um covering 14 arcsec on the MICADO field of view
Contents:
Installation
pip install anisocado
Basic Usage
Note
See Getting Started for a more in-depth introduction
Warning
This is still the alpha release of AnisoCADO.
We will attempt to maintain backwards compatiblity, however we cannot guarantee that the API will remain the same as the package evolves.
The most needed functionality is based around the AnalyticalScaoPsf class.
Create one like this
from anisocado import AnalyticalScaoPsf
psf = AnalyticalScaoPsf(N=512, wavelength=2.15) # wavelength in um
where (for the moment) N is the side length of the PSF kernel image and
wavelength is the central wavelength [um] of the PSF that we wish to
simulate.
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
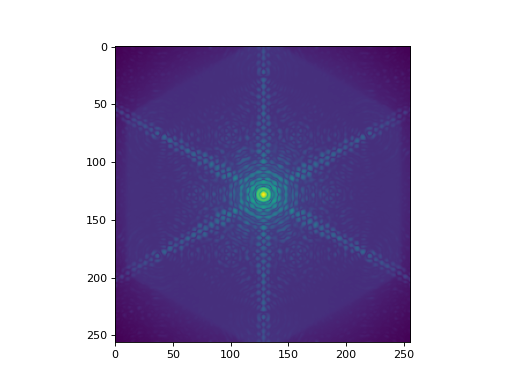
When we create an AnalyticalScaoPsf object, an initial PSF is created that is
on-axis. This can be accessed with the .psf_on_axis attribute.
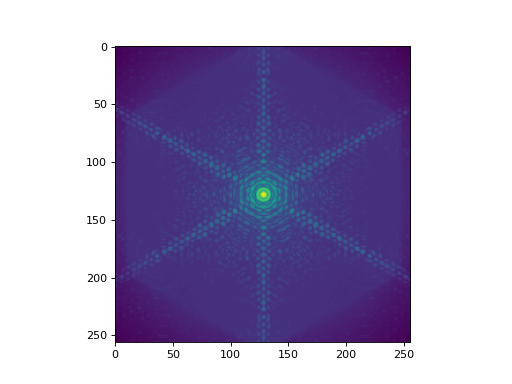
To “move” the PSF off-axis, we call the .shift_off_axis(dx, dy) method.
Here dx, dy are in arcseconds.
psf.shift_off_axis(15, -10)
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
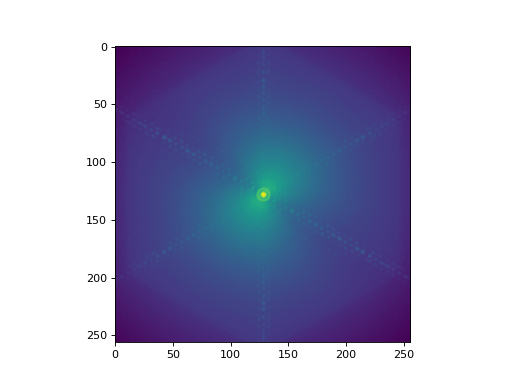
We can access this PSF in two ways: as a numpy array with .kernel or as an
astropy ImageHDU object with .hdu. Here the kernel is kept in the
.data attribute, while the header contains all the parameters used to
create the PSF kernel:
psf.kernel
psf.hdu.data
Write PSF to a FITS file
Given that the PSF can create an astropy ImageHDU object, we can take
advantage of the astropy functionality and and override the .writeto()
method of an astropy ImageHDU object:
psf.writeto("My_SCAO_PSF.fits")
Obviously this will only work for single PSFs. We will normally want to create
multiple SCAO PSFs for different wavelengths and different positions over the
field of view. To do this we can simply loop over a series of coordinates and
add the HDUs to an astropy HDUList object.
from astropy.io import fits
psf = AnalyticalScaoPsf(N=256, wavelength=2.15) # um
hdus = []
for x in np.arange(-25, 26, 12.5):
for y in np.arange(-25, 26, 12.5):
psf.shift_off_axis(x, y)
hdus += [psf.hdu]
hdu_list = fits.HDUList(hdus)
hdu_list.writeto("My_bunch_of_SCAO_PSFs.fits")
Change Log
- 2023.07.10 :
Release 0.3.0
Rename MAORY to MORFEO
Support Python 3.8 to 3.11
Fix Read The Docs
- 2023.05.03 :
Release 0.2.3
Switch to
pyproject.tomlSupport Python 3.7 to 3.11
- 2023.02.01 :
Fix bugs to support numpy 2.24
Release 0.2.2
- 2021.10.21 :
Upgraded Numpy dependency to v1.17 to use
numpy.random.default_rngRemoved support for Python 2.7